412 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Human Biology Excerpts for BBIO 053 Biology Diagrams Learn about the three major checkpoints in the eukaryotic cell cycle that ensure its proper progression and respond to DNA damage or chromosome defects. The G1, G2/M, and spindle checkpoints are regulated by cyclin-dependent kinases and cyclins. Learn about the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle and prevent abnormal cell division. Explore the roles of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and checkpoint proteins in controlling the cell cycle phases and responding to DNA damage.

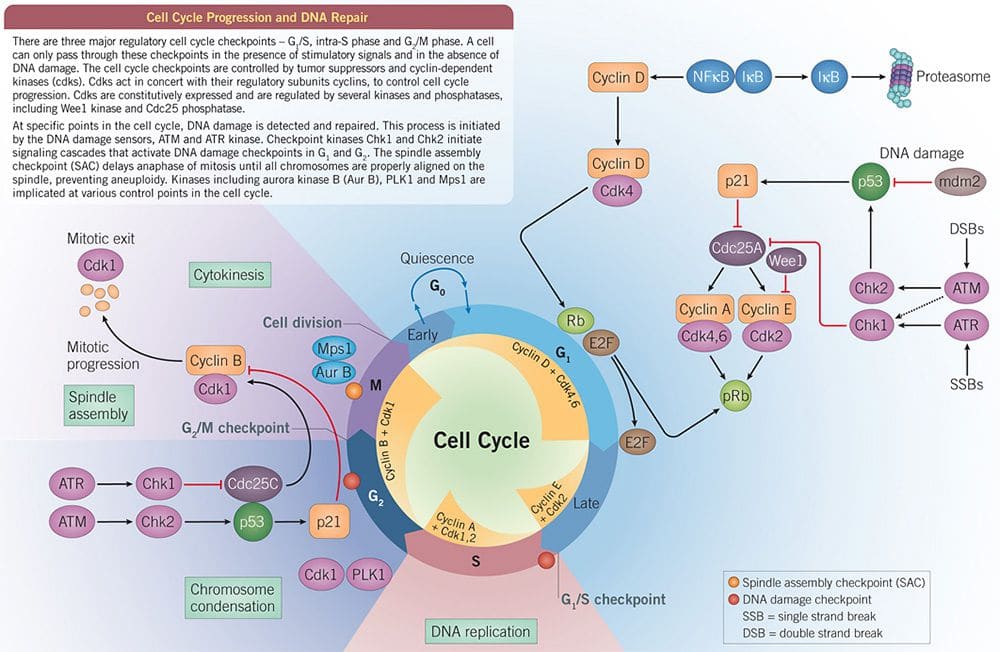
In Summary: Cell Cycle Checkpoints. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: one near the end of G 1, a second at the G 2 /M transition, and the third during metaphase. Positive regulator molecules allow the cell cycle to advance to the next stage.
Cell cycle checkpoint Biology Diagrams
Learn about cell cycle checkpoints and their role in regulating the cell cycle. A hallmark of the human cell cycle in normal somatic cells is its precision. This remarkable fidelity is achieved by a number of signal transduction pathways, known as checkpoints, which monitor cell cycle progression ensuring an interdependency of S-phase and mitosis, the integrity of the genome and the fidelity of chromosome segregation.

Checkpoints and regulatory proteins control cell cycle progression, ensuring each phase is completed accurately before advancing. These checkpoints detect errors such as DNA damage, incomplete replication, or misaligned chromosomes.

7.4: Cell Cycle Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
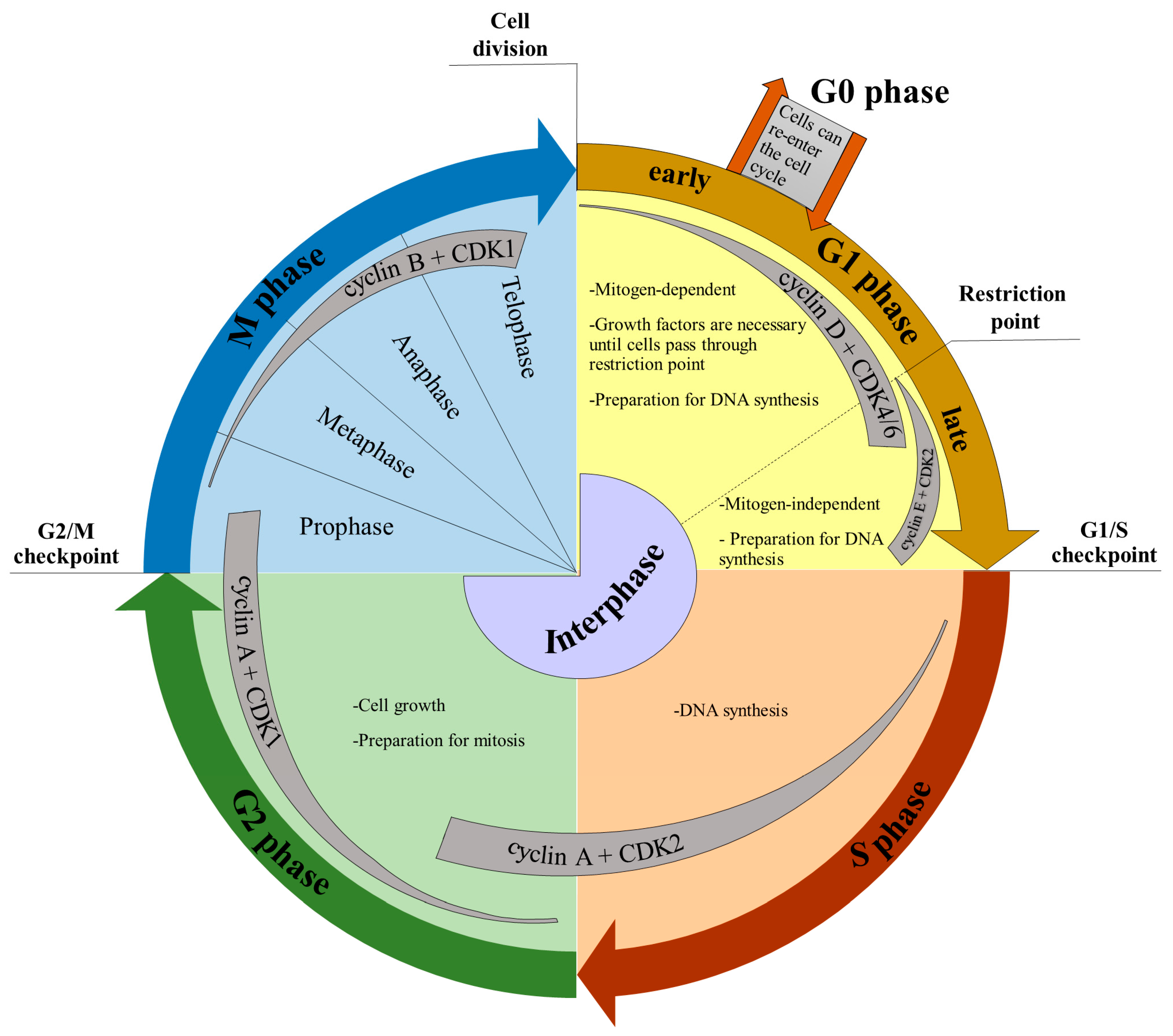
Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that results in cell growth and division. Find out the phases, regulators, and checkpoints of the cell cycle, and how they differ in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. The cell cycle includes several checkpoints, where the major ones are the G 1, G 2 and M checkpoint. G 1 checkpoint - size and nutrient verification. This checkpoint, also called the restriction checkpoint, takes place between the G 1 and the S phase. The cell verifies that it is large enough to divide, that its DNA is intact, and if there is