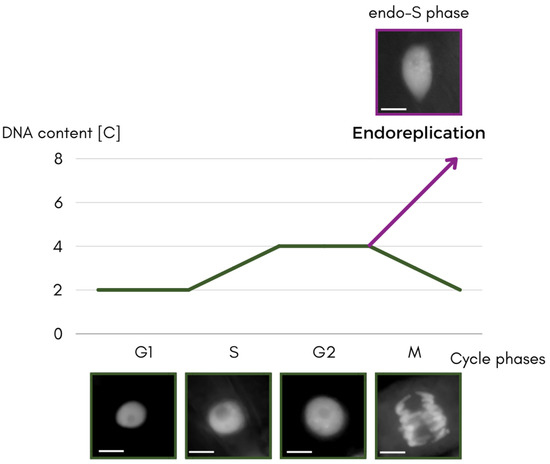
Endoreplication mediates in control of differential cell elongation and Biology Diagrams Endoreplication, an Alternative Cell Cycle Program The cell cycle is spatiotemporally regulated in multicellular organisms, the precision of which ensures that the daughter cells maintain the same amount of genetic content as the mother cell. The most common cell cycle progression is the G1-S-G2-M cycle, or the 'mitotic cycle' (Figure One common cell cycle variant is the endoreplication cycle, in which cells increase their genomic DNA content without dividing. Although endocycles are sometimes dismissed as an evolutionary peculiarity, they are widespread in protists, plants, and many animals including arthropods, mollusks, and mammals. Endocycling cells can become incredibly

Endoreplication is a pathway for cell development, slightly different from the classical somatic cell cycle, which ends with mitosis. Since many rounds of DNA synthesis take place within its course, endoreplication is a kind of evolutionary compensation for the relatively small amount of genetic material that plants possess. Endoreplication (also called endocycle) is a common cell cycle variant that frequently occurs in the cells of various tissues at specific developmental stages in animals and plants, which only comprises of DNA synthesis (S) and Gap (G) phases (1-5).Unlike mitotic cells, endoreplicating cells undergo multiple rounds of DNA replication but lack mitotic events, such as chromosome segregation

Cytokinins promote onset of endoreplication by controlling cell cycle ... Biology Diagrams
In animals and plants, DNA polyploidization widely occurs through repeated rounds of DNA replication in the absence of cell division. 1 Endoreplication (also called endoreduplication) is one type of DNA polyploidization, in which the endocycle drives only the S and G phases of the cell cycle, generating cells with polyploid nuclei. In plants, over 70% of angiosperms exhibit endoreplication Endoreplication, also called endoreduplication or endopolyploidization, is a cell cycle variant in which the genome is re-replicated in the absence of mitosis causing cellular polyploidization. Despite the common occurrence of endoreplication in plants and the tremendous extent in specific tissues and cell types such as the endosperm, the Endoreplication, an alternative cell cycle program. The cell cycle is spatiotemporally regulated in multicellular organisms, the precision of which ensures that the daughter cells maintain the same amount of genetic content as the mother cell. The most common cell cycle progression is the G1-S-G2-M cycle, or the 'mitotic cycle' . The mother
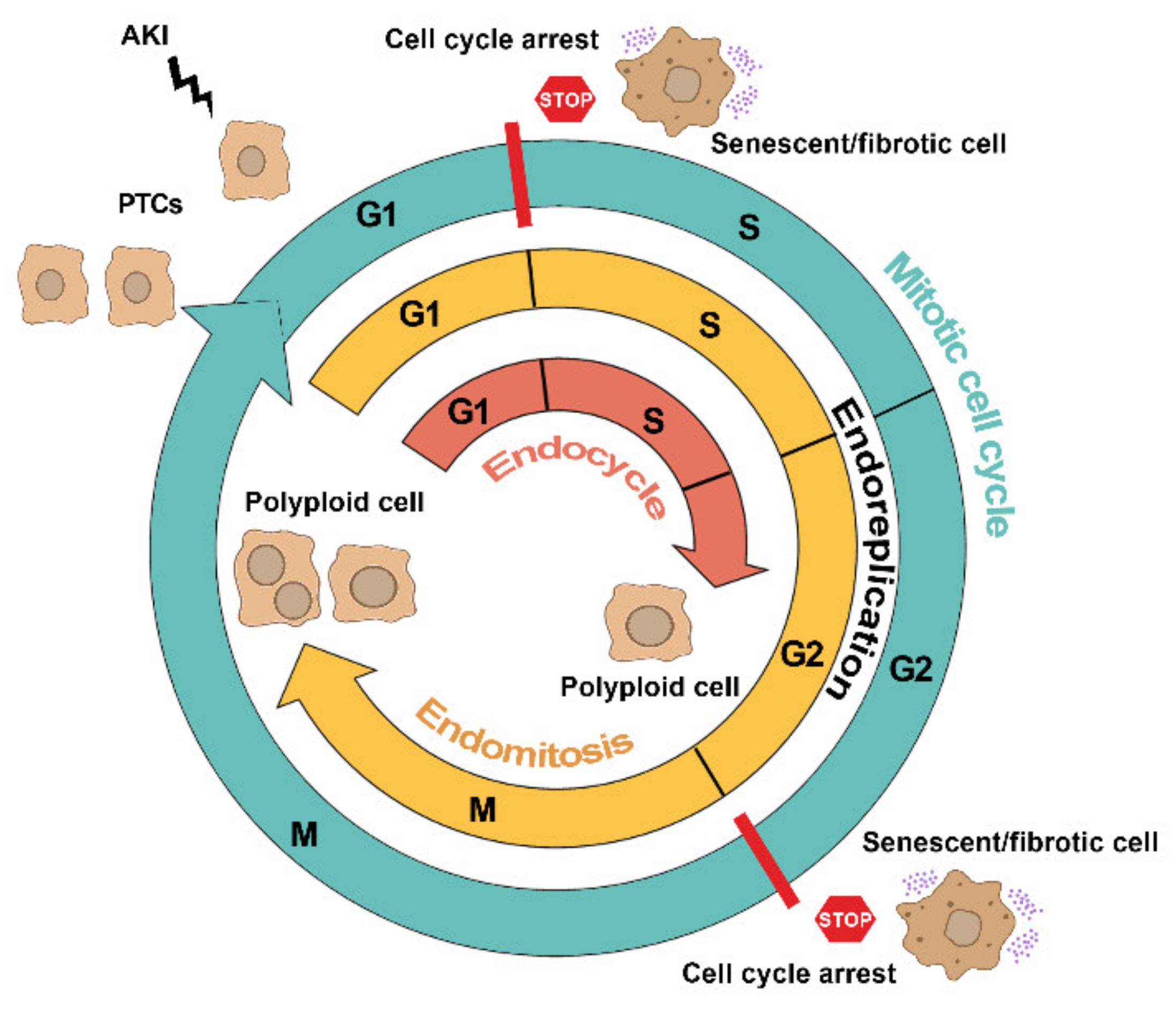
Endoreplication, in a broad sense, is a consequence of a cell division block in the presence of an active cell cycle, and it typically occurs as cells differentiate terminally to fulfill a Endoreplication is an evolutionarily conserved cell cycle program during which cells replicate their genomes without division, resulting in polyploid cells. Importantly, endoreplication is reported to be indispensable for normal development and organ formation across various organisms, from fungi to humans.