Food chain in ecosystem Biology Diagrams 2. Define a food web and explain how it differs from a food chain. Answer: A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem. It consists of multiple species that can occupy more than one trophic level, and it shows the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem. A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (Figure 8.3). In a freshwater aquatic ecosystem like a pond, the organisms in the food chain include algae, small animals, insects and their larvae, small fish, big fish and a fish-eating bird or animal (Figure 8.4). A food chain
Several crucial factors influence how long food chains can grow: 1. Ecosystem Type. Different types of ecosystems can support various food chain lengths. Terrestrial ecosystems, such as forests, typically have longer food chains compared to deserts, which can be more simplistic in their food web structure. 2. Biodiversity

How Do We Survive in Balance? Ecosystems and Food Chains Biology Diagrams
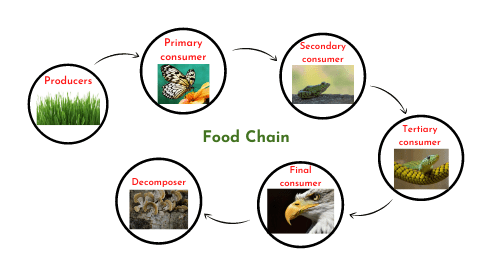
In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher-level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through the chain. Each organism in a food chain occupies what is called a trophic level. Depending on

A food chain follows the path of energy as it is transferred from species to species within an ecosystem. All food chains begin with the energy produced by the sun. All food chains begin with the

Definition, Examples, Types Biology Diagrams
The Essence of the Food Chain. A food chain is a linear sequence demonstrating how energy and nutrients flow through different organisms in an ecosystem. It articulates the relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers, each playing a crucial role in the energy transfer process. Key Components of the Food Chain Ecosystems have no particular size. An ecosystem can be small, like inside a tree trunk, medium like a pond, or large like the ocean. Food Chain. It is agreed that the living organisms need food to survive, but how do the living organisms in the ecosystem get food? The food chain explains how living things get the food they need. Food Chains. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher-level consumers, and finally decomposers. These levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through a
