Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 1 and 2 An Ocean of Food Chains and Food Webs Biology Diagrams Heavy metals such as chromium will build up in a clam's flesh over time without killing it, leaving it dangerous for human consumption. More often, seasonal microorganism blooms make clams unsafe to eat. Dynoflagetllates, a type of single-celled photosynthetic animal are a natural part of the plankton food chain. The primary consumers in the aquatic food chain are usually herbivorous animals that feed on microscopic or macroscopic algae and even bacteria. This level is usually made up of zooplankton and other herbivorous organisms. Specific empales of primary consumers in the food chain of the ocean are small crustaceans, the larvae of larger animals Introduction to Ocean Food Chains Imagine diving beneath the waves, where life moves in a mesmerizing dance of survival and collaboration. The ocean is not just water—it's a living, breathing system, powered by intricate food chains that keep everything in balance. From the tiniest microscopic plants to awe-inspiring predators like great white sharks, every creature

Let's dive into the world of clams and uncover the ripple effects of harvesting on ecosystems and food chains. Clam Ecology It's like having millions of miniature treatment plants scattered across the ocean floor. Their waste, rich in nitrogen and phosphorus, fertilizes the seabed. This nutrient recycling supports the growth of algae

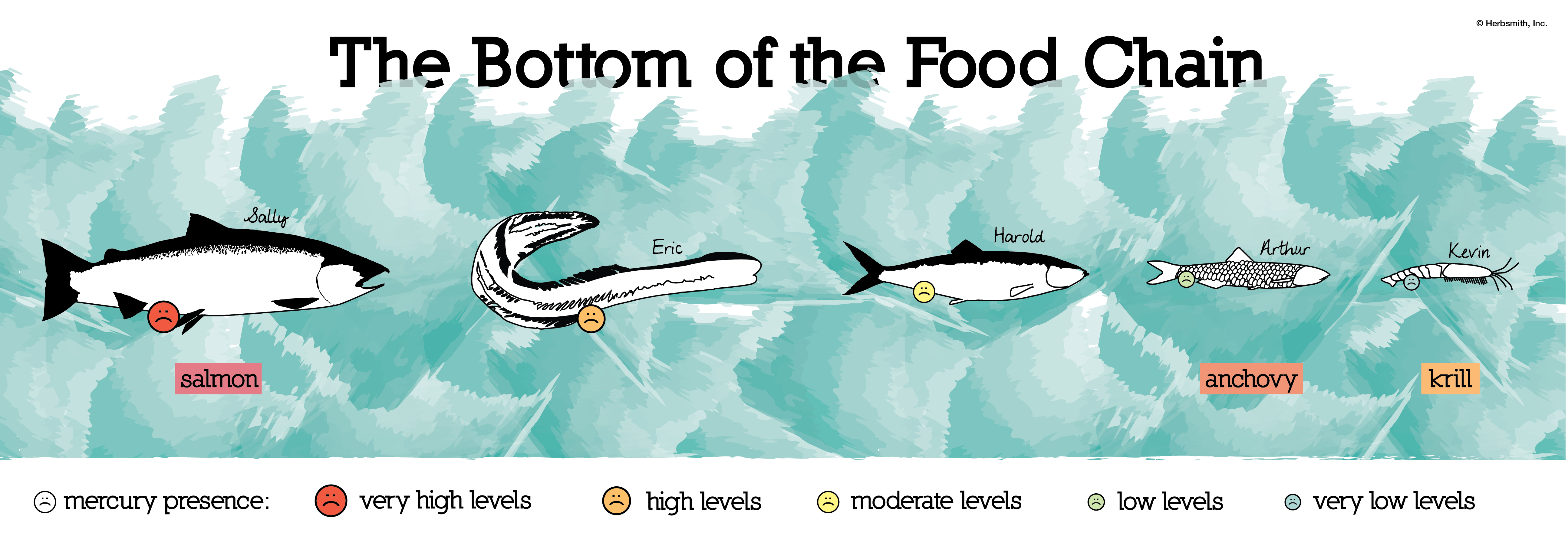
Marine Food Chains and Biodiversity Biology Diagrams
Ask: What is a food chain? Ask students to list the organisms in a terrestrial or aquatic food chain that they are familiar with. Explain to students that the trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies on the food chain. An organism's trophic level is measured by the number of steps it is away from a primary producer/autotroph Small fish, crustaceans, and worms may use clam burrows for shelter and protection from predators. 4. Food Source for Predators Clams are an important food source for a variety of aquatic and terrestrial predators. Birds, fish, crabs, and certain mammals feed on clams, which are a key part of the food web in many ecosystems. Once the shell is breached, they extract the soft clam body and eat the nutritious flesh. Clams that are too big to dismantle are buried and left to decompose before being eaten. Hermit crabs sometimes take up residence in empty clam shells for protection. The rich flesh of clams provides nourishing food for crabs across many species.