How to Read a CT Scan 8 Steps with Pictures Biology Diagrams Fully annotated brain CT - Normal anatomy of the head on a cross-sectional cranial CT Scan (axial, sagittal and coronal): brain, bones of skull, paranasal sinuses, vasculary territories, cranial base. Menu MY ACCOUNT e-Anatomy Human anatomy atlas IMAIOS DICOM Viewer Free DICOM viewer vet-Anatomy Veterinary anatomy atlas Anatomical structures Computed tomography (CT) scanning is an extremely common imaging modality in modern medicine.With advancements in technology, it is rapidly replacing many diagnostic radiographic procedures. In this article, we will outline the basic science behind CT scans, describe the principles of interpretation, and highlight their advantages and drawbacks compared to other imaging techniques.

CT brain - image orientation. Hover on/off image to show/hide findings. Tap on/off image to show/hide findings. Click image to align with top of page. CT brain - image orientation. Roll over the image (tap - mobile devices) to show the annotations; Note the side markers - RIGHT on the viewers LEFT; ANTERIOR brain/head = top of image Normal chest x ray. Radiological anatomy is where your human anatomy knowledge meets clinical practice. It gathers several non-invasive methods for visualizing the inner body structures. The most frequently used imaging modalities are radiography (X-ray), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).X-ray and CT require the use of ionizing radiation while MRI uses a magnetic The Sectional Anatomy Study Tool is a web-based program to help the user learn human anatomy through images produced by CT-scan (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). The user can easily navigate through the stacks of image "slices" of each body section. The label "on" / "off" feature provides users an opportunity for self-assessment.…
Radiology Reference Article ... Biology Diagrams
This article lists a series of labeled imaging anatomy cases by body region and modality. Brain CT head: non-contrast axial CT head: non-contrast coronal CT head: non-contrast sagittal CT head: non-contrast axial with clinical questions CT e-Anatomy is a high-quality anatomy and imaging content atlas.It is the most complete reference of human anatomy available on the Web, iPad, iPhone and Android devices. Explore detailed anatomical views and multiple modalities (over 8,900 anatomic structures and more than 870,000 translated medical labels) with images in CT, MRI, radiographs, anatomical diagrams and nuclear images. CT Scan Anatomy Overview. CT scans, or Computed Tomography scans, are essential tools in modern medicine. They provide detailed images of the inside of your body and are particularly useful for diagnosing conditions that affect the bone and soft tissues. Understanding CT scan anatomy is crucial for interpreting these images accurately.
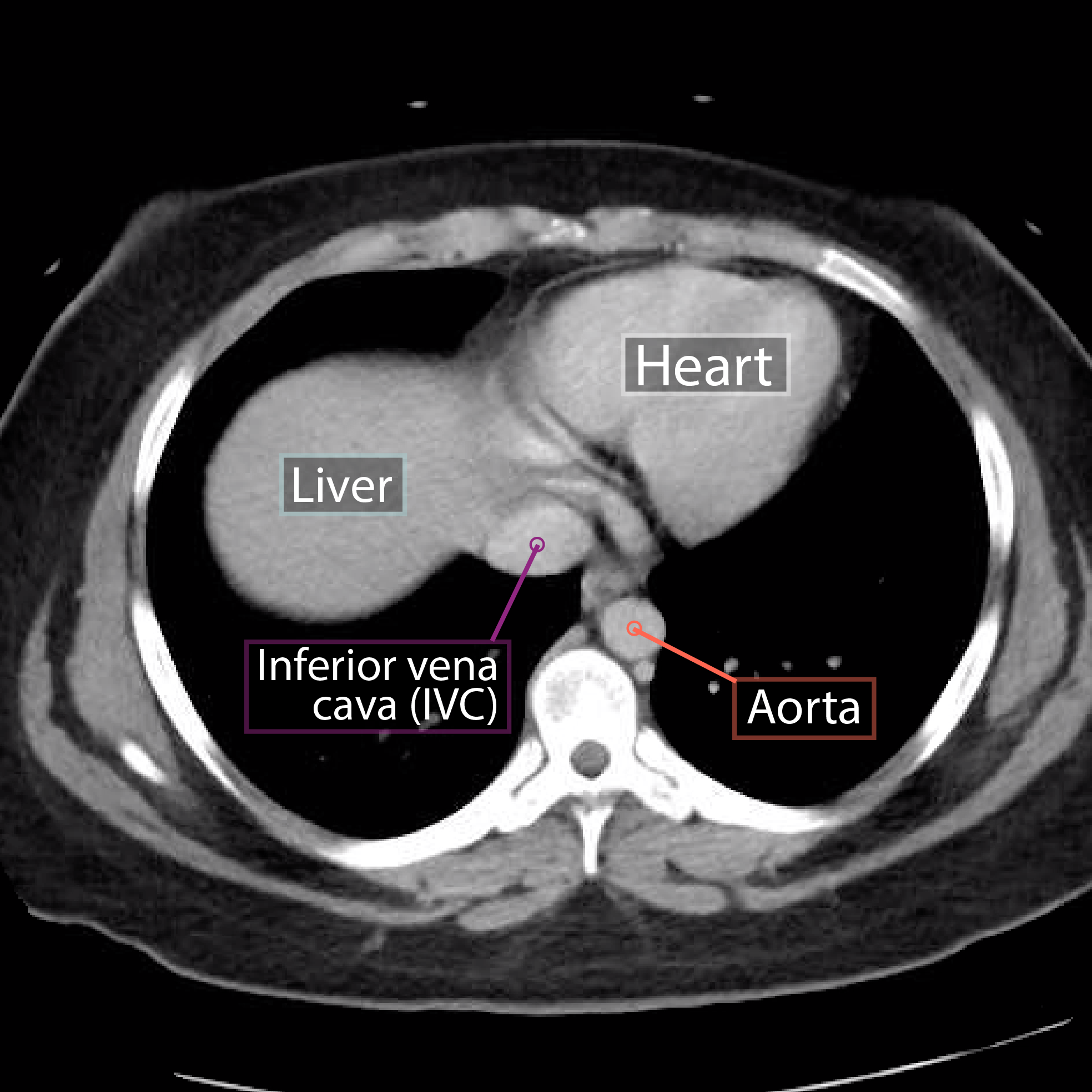
The data sets were designed to serve as (1) a reference for the study of human anatomy, (2) public-domain data for testing medical imaging algorithms, and (3) a test bed and model for the construction of network-accessible image libraries. The CT data consist of axial CT scans of the entire body taken at 1mm intervals at a pixel resolution The CT scan brain anatomy is a complex and fascinating field of study, offering a detailed look into the structure and function of the human brain. Through the use of computed tomography (CT) scans, medical professionals can visualize the brain's anatomy, identifying various structures, vessels, and pathways.
