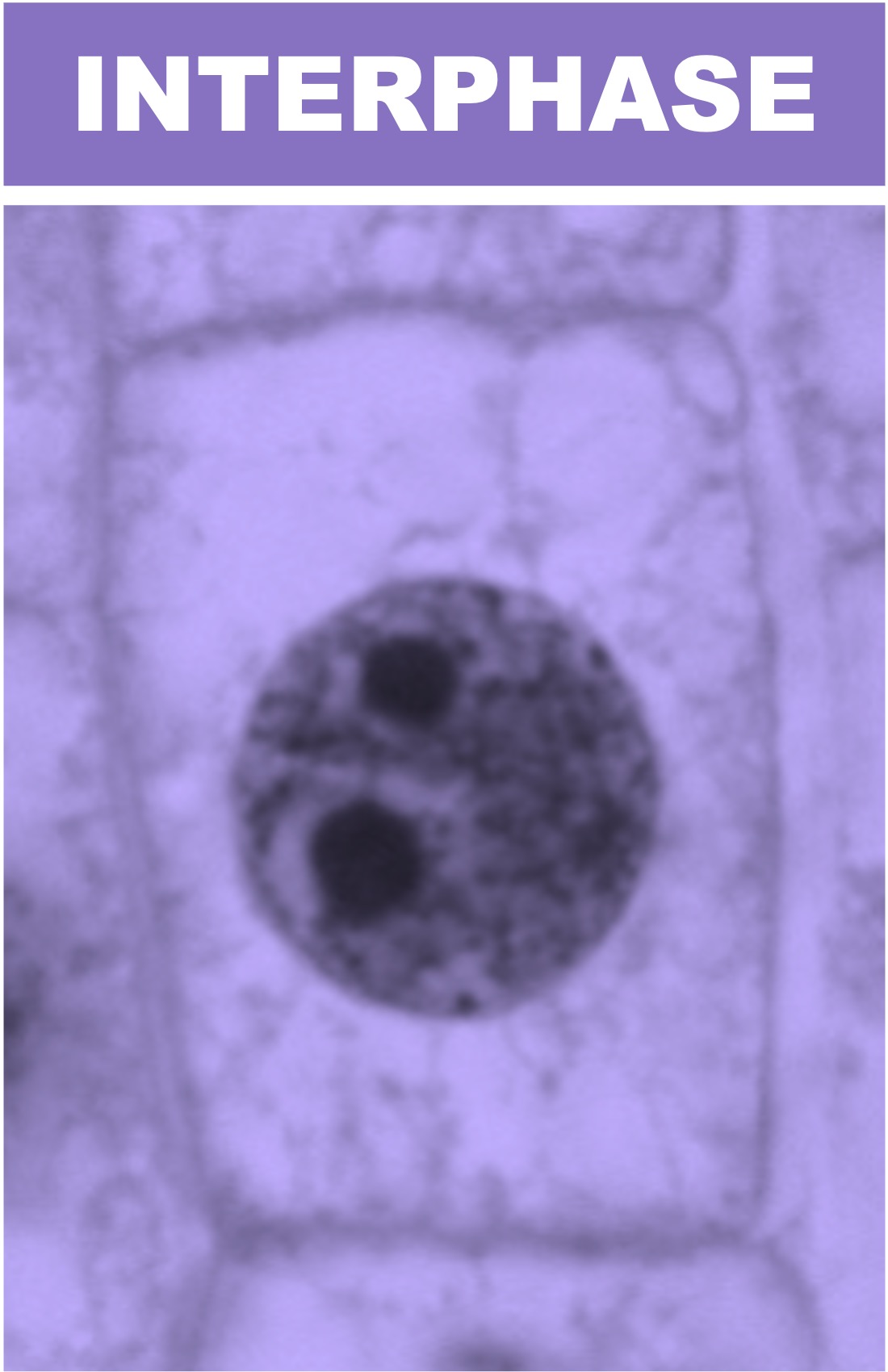
Interphase mitosis cytokinesis CIE Alevel Biology Biology Diagrams Mitosis consists of karyokinesis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and cytokinesis. 3. The chromosomes are more condensed distinct rod like structures and is thickest during metaphase. 4. It extends for a short time accounting 5% of total duration of the cell cycle. Interphase 1. It is the phase between two successive mitotic division. 2. Figure 10.6 G2 of Interphase - The last stage of interphase is the second gap period, G2. During this stage, cells grow, replenish energy and synthesize needed macromolecules, such as proteins and lipids. Mitosis - When G2 is complete, the cell will enter mitosis. Although there are 5 phases in mitosis, with the exception of the metaphase to anaphase transition, these phases are not discrete

Our complete guide goes deep on the 4 mitosis phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. CALL NOW: +1 (866) 811-5546. PrepScholar Advice Blog ☰ In fact, in the grand scheme of the cell cycle, mitosis is a much shorter phase than interphase. (Kelvinsong/Wikimedia Commons) Phase 1: Prophase. Prophase is the first step of mitosis. The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase (Figure 1). During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. During the mitotic phase, the replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. Figure 1: A cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner. During interphase, G1 Interphase, the period preceding mitosis, is the longest phase of the cell cycle and has three distinct sub-stages. G1 Phase (Gap 1): This is the phase right after cell division. Cells increase in size, produce RNA and synthesize proteins. Importantly, this phase ensures that everything is in place for DNA synthesis to occur in the next phase

Difference between Mitosis and Interphase Biology Diagrams
In order for a cell to move from interphase into the mitotic phase, many internal and external conditions must be met. The three stages of interphase are called G 1, S, and G 2 . Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): The Stages of Interphase and the Cell Cycle: The cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. During interphase, the cell grows "The first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis. G1 phase ends when the cell moves into the S phase of interphase. Around 30 to 40 percent of cell cycle time is spent in the G1

Before a dividing cell enters mitosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. About 90% of a cell's time in the normal cell cycle may be spent in interphase. G1 phase: The period before the synthesis of DNA. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. The G1 phase is the first gap phase. During interphase, the cell grows and performs its functions. In this phase we find three different subphases: G1: Subphase in which the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication. S: subphase in which the cell replicates its DNA. G2: Second phase of growth in which the cell prepares for cell division or mitosis. M: phase known as mitosis that Not all cells adhere to the classic cell-cycle pattern in which a newly formed daughter cell immediately enters the preparatory phases of interphase, closely followed by the mitotic phase, and cytokinesis. Cells in G 0 phase are not actively preparing to divide. The cell is in a quiescent (inactive) stage that occurs when cells exit the cell cycle.