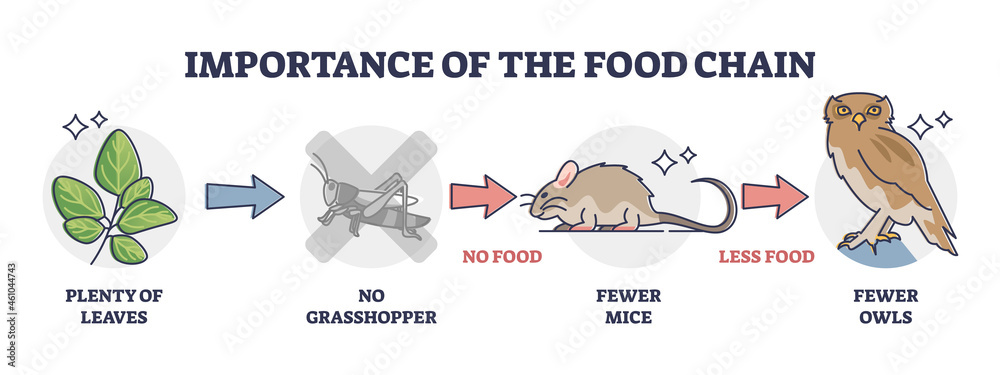
Science online The effect of the extinction on the ecological equilibrium Biology Diagrams The species was thought to be extinct in Australia for about 10,000 years, but a re-examination of a 100-year-old specimen in 2012 has suggested that the creature may have existed as recently as The loss of a single species from its ecosystem affects other species that rely on it. The disappearance of one plant species may affect an entire food chain, starting with insects that live or feed on the plant, moving on to the birds and frogs that eat the insects, and ending with the larger animals like snakes, hawks, and foxes that prey on the birds and frogs. Trophic Cascades: The Domino Effect. One of the most profound impacts of endangered species on the environment is the phenomenon known as a trophic cascade.This occurs when the decline of a species at one level of the food web has repercussions throughout the entire chain.

A food web, according to the U.S. Geological Survey, is "who eats what." Also called the food chain, the food web describes the series of relationships that occur between predators and prey in an ecosystem. You are a member of the food web if you eat animals that have eaten other animals or plants. Species belonging to the three fauna that occupy different locations in the food chain of stream ecosystems (i.e., fish, benthic macroinvertebrates, and epilithic diatoms) were investigated and taxonomically resolved at the species level; for instance, fish were surveyed for all habitat types including riffle, pool, and run, using kick-net
11 Endangered Species That Are Still Hunted for Food Biology Diagrams
Disrupted Habitat. Extinction of animal or bird species in the food chain may alter the physical environment as well. For instance, accidental introduction of the predatory brown tree snake to Guam wiped out 10 of the 12 native bird species on the island causing collateral damage to the forest, according to a University of Washington study. The strong body of knowledge accumulated in recent decades has shown that endangered species lists are only the most visible side of a more insidious kind of threat cast over the natural food webs that support life on Earth (Memmott, 2009; Tylianakis et al., 2010; Valiente-Banuet et al., 2015). Here a high proportion of the primary production is efficiently consumed by primary consumers and energy transfer is shared among a small set of abundant species, effectively forming simple food chains (Shurin and Borer, 2002, Shurin et al., 2006, Strong, 1992).
